

Chemical Equations for the reaction of Pb with HCl and HSO 4 to form salts are: Thus, we can predict the reactions by reactivity series. The reaction between metals and acids – Lead and other metals which are more reactive than lead in the reactivity series can react with hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid and form salts. Note: Ca virtually remains unreactive with cold water however, it forms calcium hydroxide with a release of half a mole of H 2 gas. The resultant solution is basic because of the dissolved hydroxide.Ĭa + H 2 O (l) → Ca(OH) 2 (aq) + ½ H 2 (g)Ĭalcium Cold Water Calcium Hydroxide Hydrogen Note: Potassium reacts extremely violently with water to form a colourless aqueous solution of KOH with a release of12mole of H 2 gas. Potassium Cold Water Potassium Hydroxide Hydrogen The reaction between metals and water – Metals from potassium to calcium can react with cold water and release hydrogen gas.Ĭhemical Equations for the reaction of K and Ca with cold water are:

So, by reactivity series, you can tell which metal will displace another metal. In displacement reaction – Displacement reactions are those reactions in which more reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its salt. When we move down the series the electron-donating capacity of metals decreases. While metals from Zinc to Hg can be extracted by simply reducing their oxides, which is an inexpensive method. The metals which are placed above in the series can be extracted by electrolysis. Thus, metals placed at the top of the reactivity series can remove the metals which are present at the bottom of the series from their salts. The metal which is more reactive than other metals can remove less reactive metal from its salt.

Metals present in the reactivity series above hydrogen can remove hydrogen ions from dilute HCl or Dilute sulphuric acid. Thus, potassium is the strongest reducing agent.Īs we go down the reactivity series, the ability of metals to remove hydrogen from hydrides decreases. The reducing power of metals decreases as we go down the series. The electropositive character of metals decreases as we go down the series. Metals present at the top of the reactivity series are highly electropositive metals. May react with some of the strong oxidizing acids May react with some strong oxidizing acids Reacts with acids very poor reaction with steam Or less commonly other alkali metals, hydrogen or calcium in the Kroll process Pyrometallurgical extraction using magnesium, In boiling water, and very vigorously with acids. Reacts very slowly with cold water, but rapidly Here is the tabular format of the same.Įlectrolysis (a.k.a.
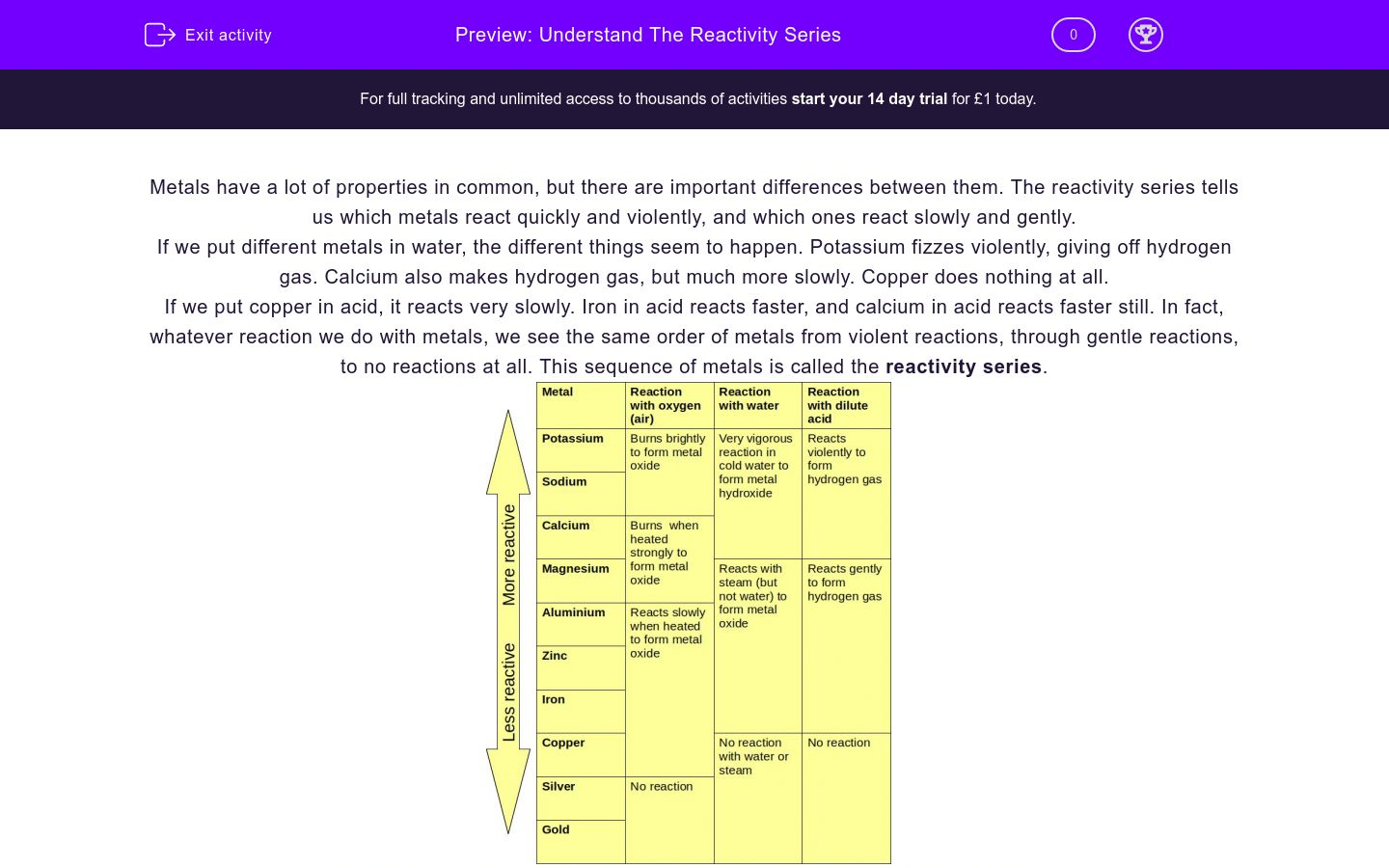
Here metals are segregated in terms of their reaction with cold water, hot water, acid, and steam and reaction with concentrated mineral acids. The reactivity of the metals is given below in another tabular format where it has been mentioned along with its ions. Hydrogen is a non-metal but still, it has been included in the reactivity series as it helps in the comparison of reactivity of metals. While metals such as zinc, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, etc. This is the reason why platinum and gold don’t get corrode easily and don’t form oxides. Metals from copper to platinum are highly unreactive and don’t react with any other substance in normal conditions. While metals from magnesium to lead can react with acids. Metals from potassium to calcium are highly reactive and even react with water.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
